The Elliptical Energy Pathway Theorem (EEPT) is a building philosophy which encourages us to think about the way energy moves through structures.
Nature is full of examples of vertically stable structures which do not, like standard man-made structures, use mass and stiffness to oppose external forces. These natural examples serve as inspiration for innovative structural designs. The EEPT has been used to explore concepts such as: coupled inverted pendulums as a model for dynamic shear-storey building behaviour under wind and earthquake actuation; using existing building mass as a self-tuning mass damper; façade designs which absorb wind actuation at the source; and textured façade elements to alter wind-building interaction.
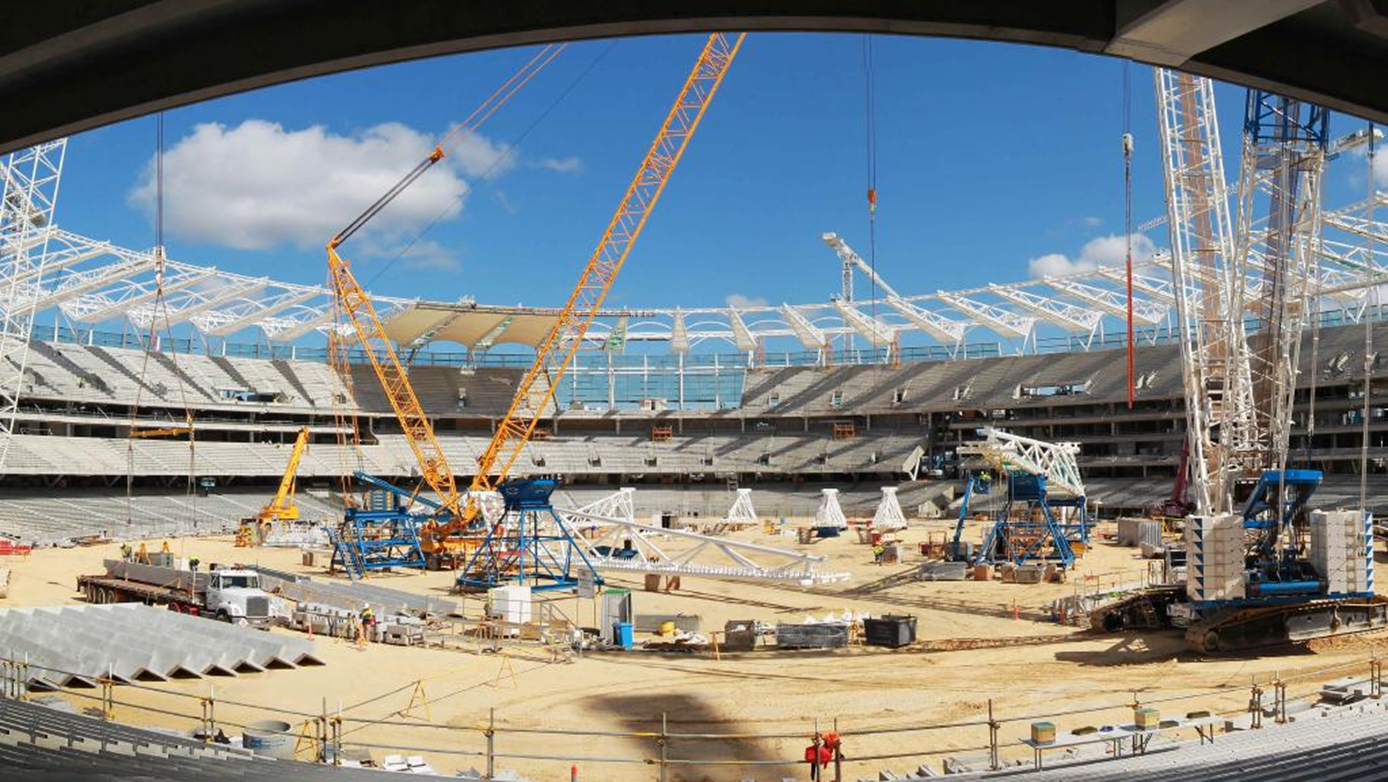
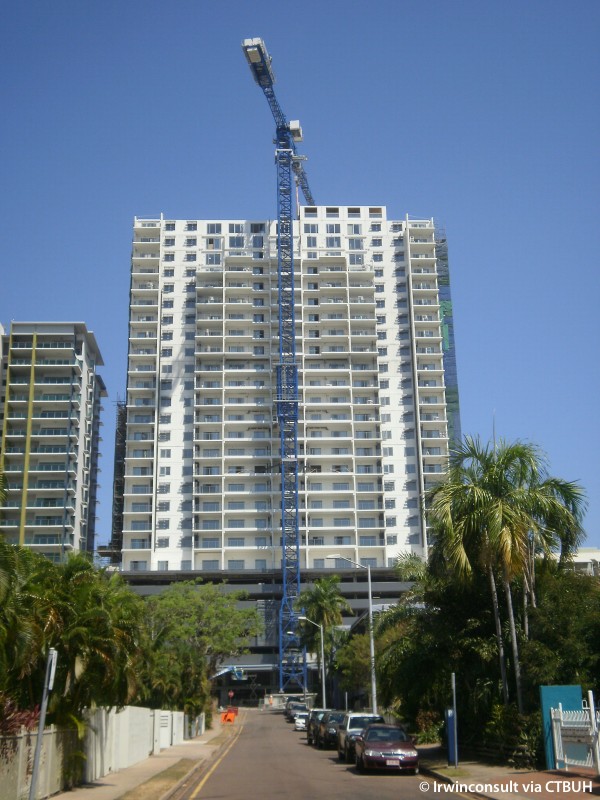







Western Australian Government, Multiplex
2014-2017
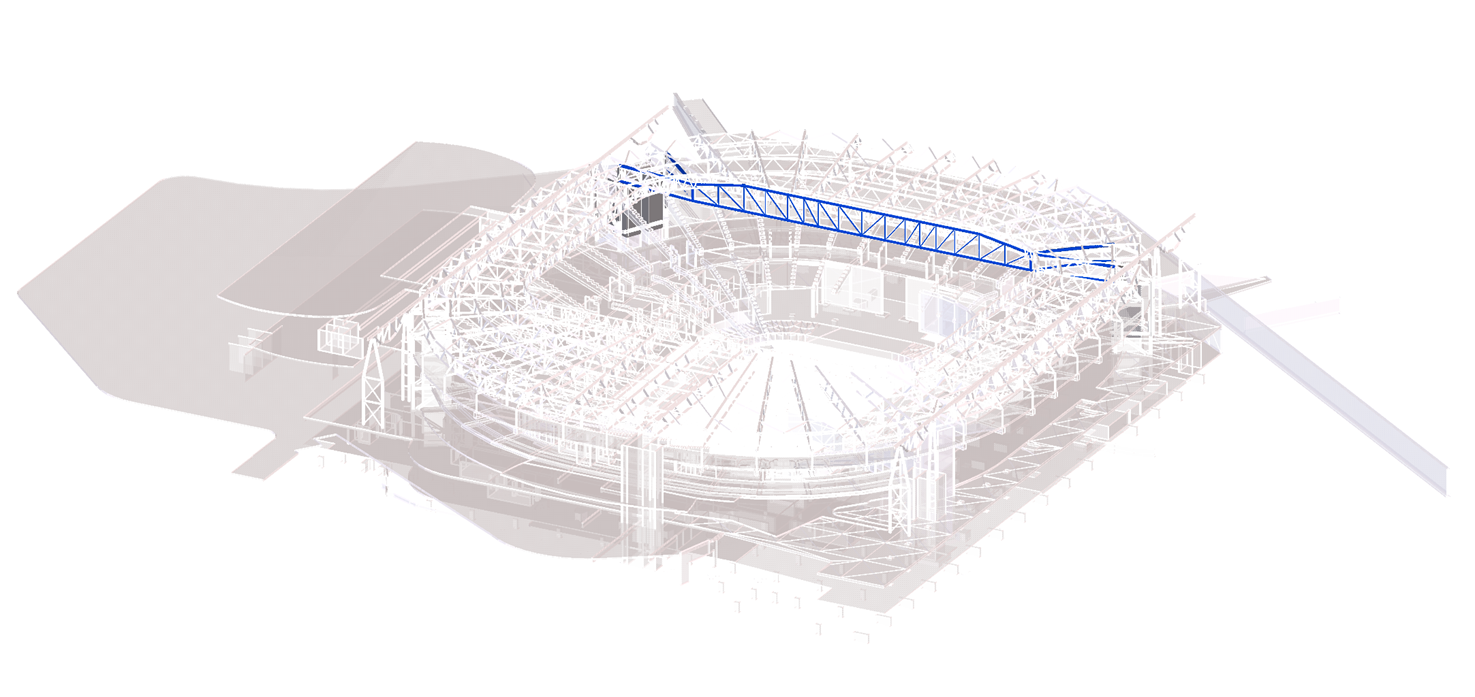
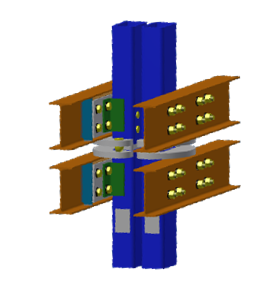
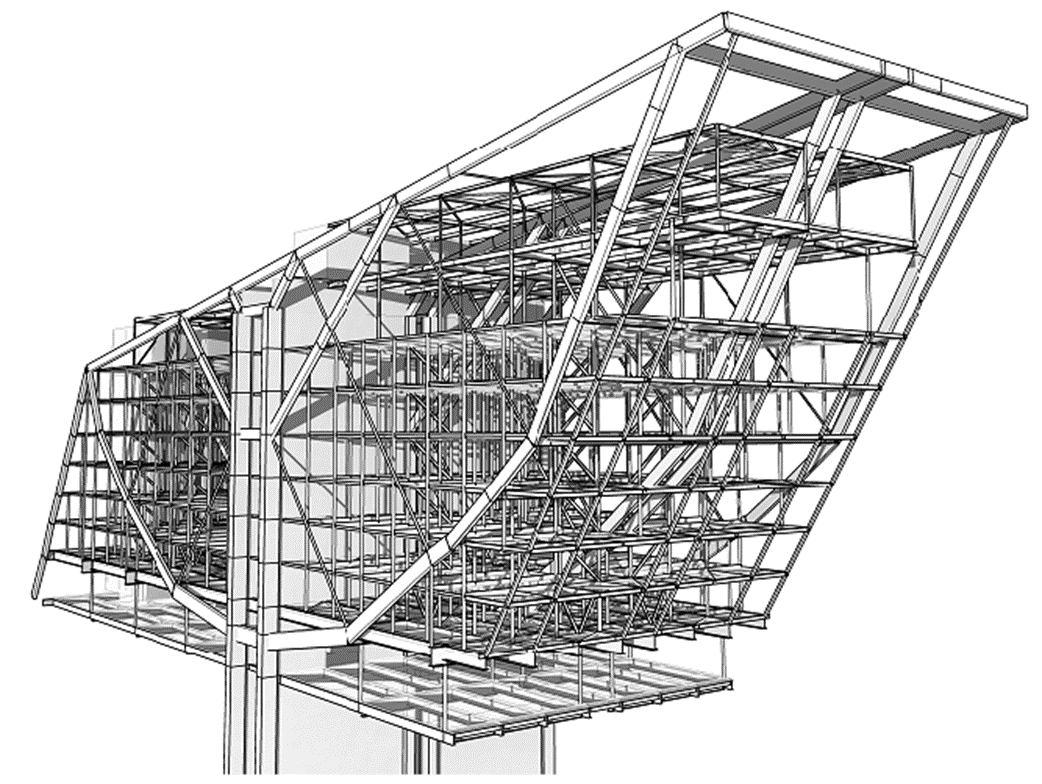
Alternative design options for Perth Stadium were developed throughout the stadium to introduce efficiencies and more appropriate material selection. Efficient connections were designed to eliminate potential issues with alignment and tolerances which in turn minimised the erection time. Redundant material was taken out where possible and alternative systems were proposed to reduce the overall mass of the project and introduce more sustainable solutions.
This involved taking inspiration from a shock absorber swingarm joint of a motorcycle, which informed the creation of a cylindrical multiple hinge truss connection to mount to the roof structure of the stadium.
World Class Global, Multiplex
2014-2020
Australia 108 is the tallest residential tower in Australia, thus the discovery and adoption of even small optimisations mean large reductions in consumed resources for the building. Various design concepts throughout the design process were proposed to improve the buildability of the structure and reduce the mass while still maintaining the overall structural integrity. A prefabrication methodology was adopted where possible to provide a more efficient construction solution.
Gwelo Developments
2012-2014
The project was designed to incorporate 22 modular floors built on a podium. Modules utilised prefabricated systems to construct the apartments and hotel suites offshore.
Concrete columns were poured in-situ into formwork provided by the steel columns built into the module walls. This carries the weight of the modules whilst locking them together resulting in transferring very high wind loads back to the core.
Total weight of each module was 26 tonnes. They were shrink wrapped in plastic before leaving the factory to provide an added layer of protection during transport. At the time of completion (2014) SOHO Tower was the tallest volumetric modular building in the world.
Meyer Timber
2014
Developed in conjunction with the Meyer Office, the concept behind the Tendon Intersect Connection & Tension Offset Cone Connection (TIC-TOCC) was invented to minimise time spent connecting panels in modular construction. The connection which was designed to provide a competitive alternative to other post-tensioned connection systems for wall panels.
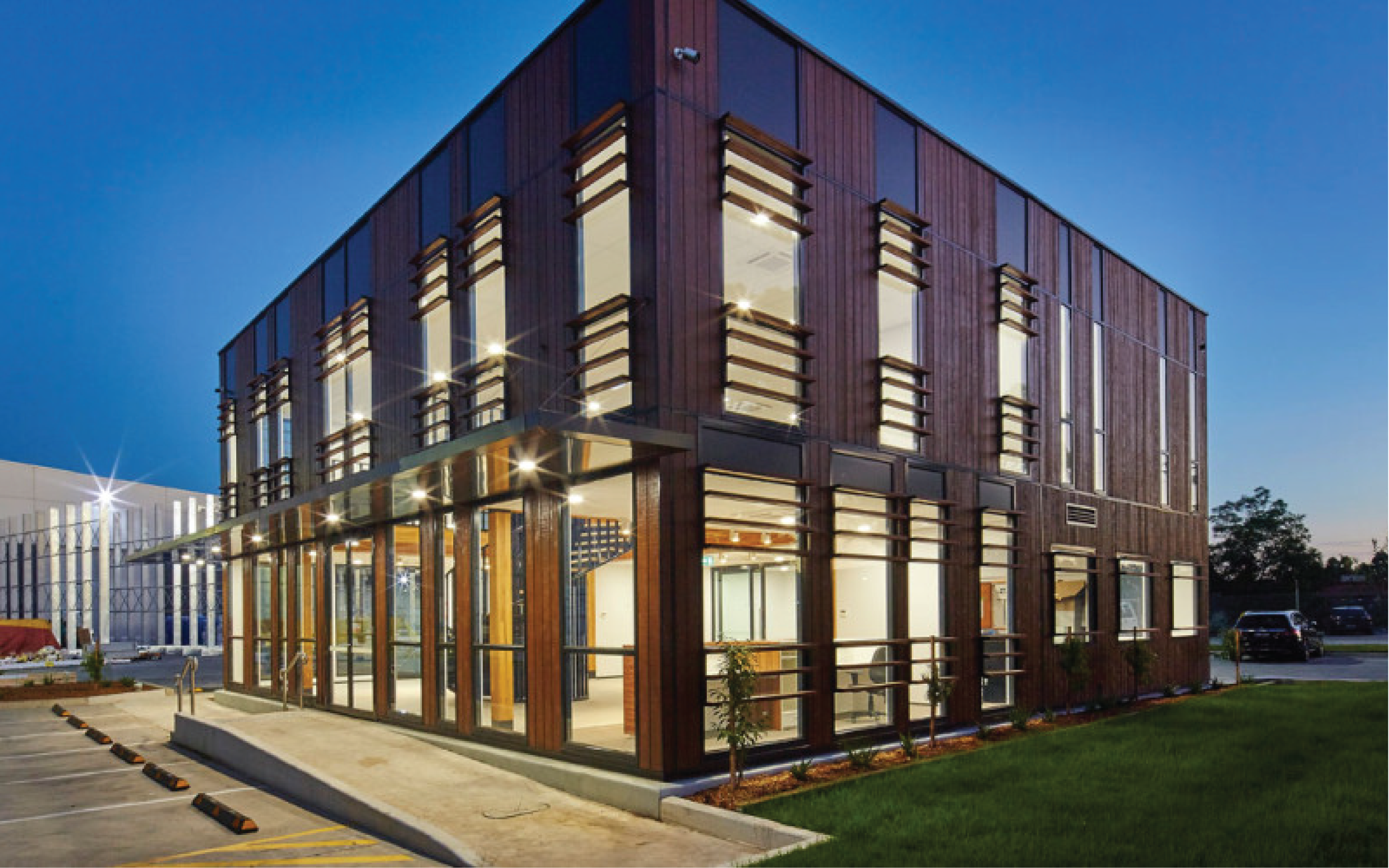
Meyer Timber
2014-2015
This project is an office building designed to implement a flat-pack DfMA construction methodology through modularisation of all the components and efficient transportation to site.
With smart connection designs (TIC-TOCC), the structure was able to be completed in 2-3 days with the roof installed on the third day, all with only a small team of engineers and riggers.
This project showcased the efficiency that can be achieved through modular design and construction.
Melbourne and Olympic Parks Trust
2015
Utilising a biomimetic approach, a structural solution was developed taking inspiration from the fine gossamer threads produced by spiders. The Gossamer Truss provided a solution to easily retrofit a structure and minimise potential clashes.
Schiavello
2017-2018
The Single Pin Expansion Connection (SPEC) was designed to provide a more efficient solution for modular construction.
The simplicity of the connection allows it to be housed within the cavity of a wall panel and locked into place within a matter of minutes.
The connection itself has undergone several iterations to improve its efficiency for future use.
Tallwood, Brookfield
2018
The BohrHaus modular construction system was conceived as a lightweight, cost effective, environmentally sustainable and modular solution for rapid construction of new buildings anywhere in the world, using off the shelf parts, such as roadside guardrail, timber bush core and threaded steel dowel.
Each column uses a threaded steel dowel connection that locks each section in place, efficiently and accurately.
Powercor
2013-2014
Precast concrete unit to pile connection. Simple & effective connections allowed for the structures to be installed accurately and quickly.
Prefabrication also allowed for many on-site issues to be resolved prior to delivery and installation of the units, whilst also allowing production to commence before completion of all design.
Hickory Group
2013
The LBC damping system was invented by James Murray-Parkes. It takes learnings from James’ research in continuous connections, his Elliptical Energy Pathway Theorem and invention of the TIC-TOCC connection shown previously.
LBC also addresses actuated forces, and how to control them, and the vibration response of the building during seismic events through various damping systems.
Along with beam-to-column bracing, the LBC damping systems creates a cooperative structure that allows all structural components to work together. Results in ability to design and construct buildings that don’t rely on a traditional core system.
Mona, Multiplex
2017
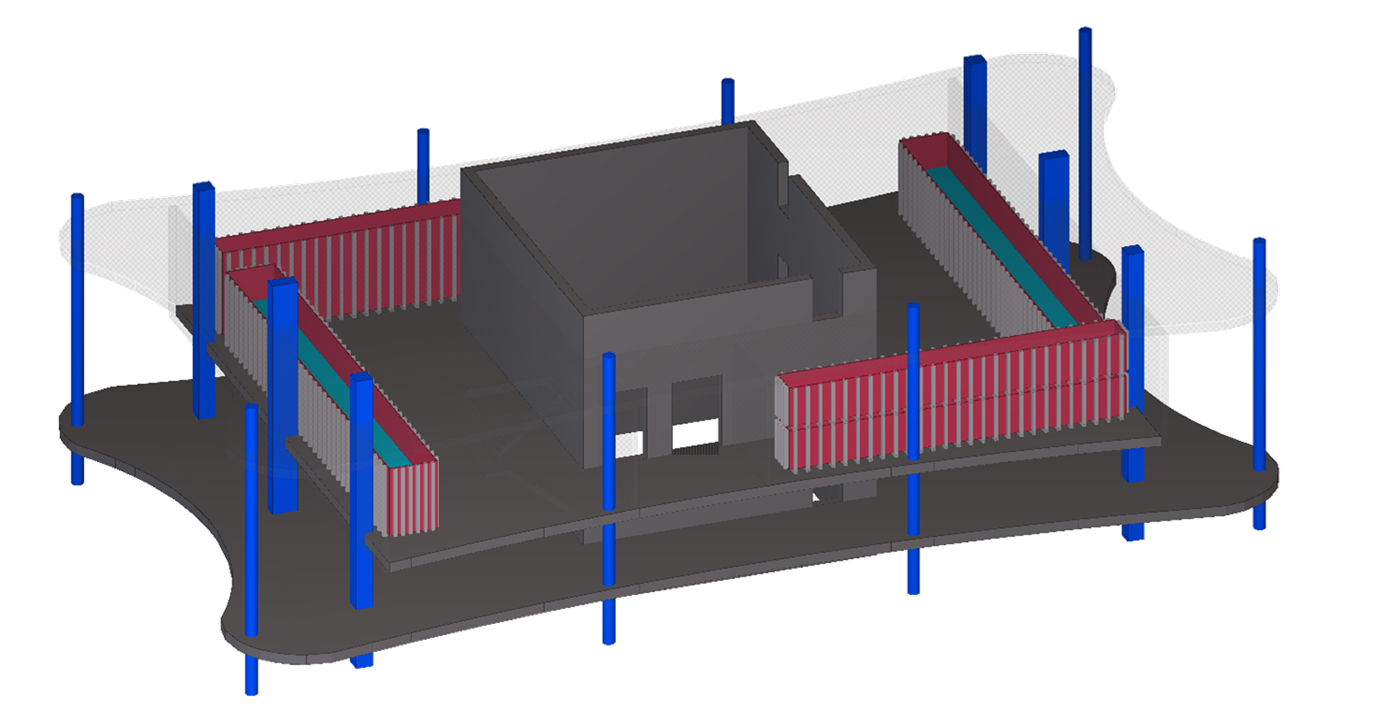
The Hotel Mona project involved the concept design and feasibility study for a new hotel on the Mona site.
The requirements of the project necessitated the development of an innovative design which was capable of achieving the extreme cantilever desired by the client, whilst utilising modular construction to reduce the complexity of on-site operations and optimise the erection sequence.
Scale physical models were produced to demonstrate the concept and communicate to client and builder alike how each element worked.
Multiplex
2018
The How to Design a Structure publication was instigated by Prof. James Murray-Parkes and the team at the Multiplex Engineering Innovations Group.
The book outlines the progress, evolution and solutions to structural design alternatives made by James and his team between 2013 and 2018. It provides an overview of the wide range of opportunities for alternative design and optimisation which are present in projects in spaces from modular construction to tall buildings and more.
Monash University, Victorian Government
2015-2017
This was initially instigated by Prof. James Murray-Parkes, Prof. Yu Bai, Adam Styles, Angela Wang, Monash University, the Victorian Government, and various industry partners.
This handbook was the first of its kind in the world, providing integrated solutions and experiences to industry, government and the community including: Design for performance; Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA); and Regulatory compliance.